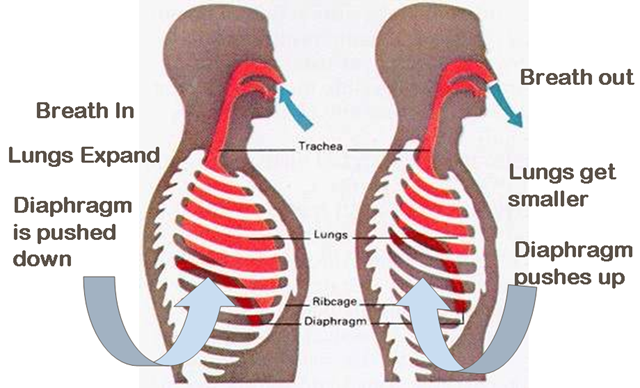
The diaphragm is the large muscle located at the
base of your lungs and above the stomach cavity. It is considered to be the
most efficient muscle of breathing and is assisted by movement of the abdominal
muscles in order to push air out of the lungs. However, when there are certain
issues with the lungs the diaphragm may be have limited power, which may require
the chest and neck muscles else to work harder than normal. Here are some tips from
the American Medical Student Association on how to focus on breathing more
efficiently through diaphragmatic breathing:
- Place one hand on your chest and the other on your abdomen. When you take a deep breath in, the hand on the abdomen should rise higher than the one on the chest. This ensures that the diaphragm is pulling air into the bases of the lungs.
- After exhaling through the mouth, take a slow deep breath in through your nose imagining that you are sucking in all the air in the room and hold it for a count of 7 (or as long as you are able, not exceeding 7).
- Slowly exhale through your mouth for a count of 8. As all the air is released with relaxation, gently contract your abdominal muscles to completely evacuate the remaining air from the lungs. It is important to remember that we deepen respirations not by inhaling more air but through completely exhaling it.
- Repeat the cycle four more times for a total of 5 deep breaths and try to breathe at a rate of one breath every 10 seconds (or 6 breaths per minute). At this rate our heart rate variability increases which has a positive effect on cardiac health.
- This exercise should be done once or twice a day at first, but the more you become accustomed to it you may do it several times each day.
Diaphragmatic breathing helps strengthen the
diaphragm, decreases the work of breathing by slowing your breathing rate, improved
stamina in both disease and athletic activity, and stimulates the relaxation
response that helps result in less stress and tension. It is an excellent
technique to help you reach a greater sense of overall wellness.

No comments:
Post a Comment